Behind the company’s phenomenal success rests a well-thought-out marketing strategy that over the years of operations has set the company apart from other top competitors, Pizza Hut and Papa John’s, and propelled the organization to the very top of the fast-food industry, thereby, making it the largest fast-food chain across the globe. The dissertation delves into crucial components of Domino Pizza’s marketing strategy, exceptionally exploring the innovative marketing strategies implemented by the organization, that have facilitated its success within the highly competitive landscape of fast food.
A slice of Domino Pizza’s History
James and Tom Monaghan, in 1960, started the Domino organization in Ypsilanti, Michigan, with the primary objective of revolutionizing the fast-food industry by the delivery of hot pizzas right to the doorstep of potential consumers – and little did the founders know that their small venture would turn out a global success. As years passed Dominos fast food in business, the organization widened its scope of business and expanded into new markets. And by the end of the 1970s, the company has established over two hundred outlets across the state, with the company having been firmly established on the international stage by the turn of the century (Išoraitė, 2016). For the Domino organization, the 2000s meant a drastic change with a modernization drive that resulted in the introduction of strategic menu selections, and the development of the company into the digital platform with the creation of mobile applications and a cutting-edge website that made the company’s services even faster and easier than before (Singh, 2012). Today, the company has established over seventeen thousand outlets across ninety nations, standing tall as one of the most reliable and largest fast-food chains across the globe. And with a firm commitment to convenience and quality, the organization continues to serve its customers with an opportunity to enjoy Domino’s Pizza and associated accompaniments.
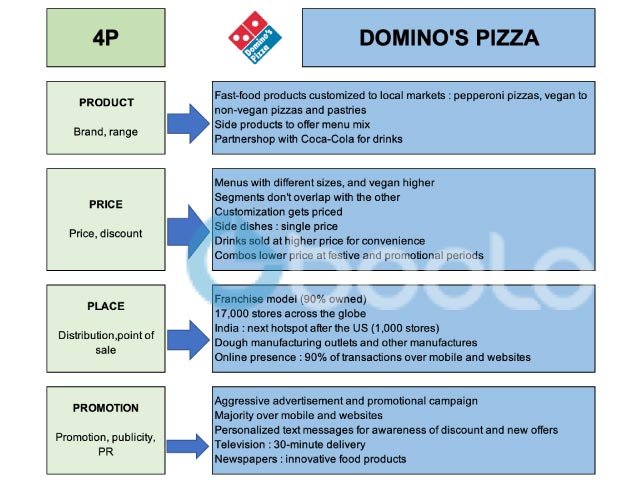
Dominos Marketing Mix (4P)
The marketing strategy implemented by Dominos analyzes the organization from a marketing mix framework that traverses the 4Ps – Promotion, Product, Price, and Place. Several other marketing strategies such as pricing approach, product innovation, and promotion planning, based on Domino’s marketing mix, have aided the company to thrive in the market. It is, therefore, reasonable that the company’s marketing strategy has helped its competitive positioning within the market with reasonable objectives and goals.
a. Domino Product Strategy
The product strategy and marketing mix the marketing strategy implemented by Domino may get explained as follows: The Dominos organization has been one of the primary pizza outlets across the globe, with the company’s product line being mainly concentrated on different types of fast-food products which get customized with respect local markets.
Within the United States, the most popular food product offered by the Dominos is pepperoni pizza; other regions have had the product ranging from vegan pizzas to other non-vegan pizzas (Išoraitė, 2016). The intricate size of the bases has had a significant variety of different types – a variety of sauces, dips, and toppings included.
Ideally, the products by Dominos may get customized as per the requirements of the consumers, with other possibilities of different kinds of pasta both vegan and non-vegan kinds.
The organization has further involved other pieces of bread apart from pizza loaves of bread and pastry made from pizza ingredients within the menu to not only encourage consumers to associate with the company but also extend the reach of the company’s products and services.
The side products offered by the organization have also involved bacon, chicken wings, and other flavored meat dishes – all of which constitute the primary product mix within the company’s marketing mix (Constantinides, 2002).
In many cases, the dishes get accompanied by drinks, for which the company has partnered with Coca-Cola and retails soft beverages and major drinks made by the Coca-Cola company. The menu offered by Dominos also primarily involves different kinds of chicken crusts, pizzas, kinds of pasta, flavored loaves of bread, side dishes ranging from chicken items, desserts, dips, and sandwiches, mousse cake, burger pizzas, and other choices of toppings.
b. Dominos Pricing Strategy
Dominos has had a commendable pricing strategy owing to the fact that the organization has two major competitors.
The prices on different fast-food products get done differentially with three sizes available to the company and the non-vegan version of products getting charged relatively higher.
Additionally, the pricing of loaves of bread and pizza, as well as other eatables within the organization’s marketing mix get done so that the segment one size does not overlap with the other (Shah, 2013). As the company goes on with the customization of its products, the charges get based on the parts added to the different products.
The side dishes, nonetheless, do not have special choices and hence get priced at a single price.
The beverages and drinks offered by Dominos have turned out quite higher compared to drinks typically sold from general markets owing to the convenience. Occasionally, the company may sell combos at relatively lower prices during festive seasons and promotional periods.
c. Dominos Place and Distribution Strategy
The fast-food giant has operated on a franchise model where about ninety-seven percent of its operations get franchise owned. At the moment, about seventeen thousand stores get operated by the company across the globe. Within the United States, the company has involved about four thousand domestic franchise outlets: internationally, over seven thousand stores have been established by Dominos.
India remains the next hotspot for the company, outside of the United States, with the destination hosting more than a thousand stores (Constantinides, 2002).
Additionally, the company has several dough manufacturing outlets and one critical equipment supply center – one vegetable processing center gets run by the company as well as one pressed plant center within the United States. A similar kind of proportion gets maintained across the globe while critical machines and other equipment get supplied by Dominos.
The company still maintains a robust presence within the online platform as over ninety percent of its transaction happen online via mobile apps and websites, with more than thirty states making orders through the website. The company utilizes its platform during delivery, as well as promotes itself on other fast-food delivery applications.
d. Dominos Promotion and Advertisement Strategy
Within its marketing mix, Dominos do advertisements and promotional campaigns more aggressively compared to its competitors, with a majority of its promotions and advertisements taking place on the company’s mobile application, and websites, as well as personalized text messages to individual consumers designed to capture attention and create awareness of discounts and new offers (Serrano et al., 2017).
The company also promotes its operations on Television services where it claims 30-minute delivery services.
In some cases, the company may feature in newspapers different innovative food products launched on its menus across the different stores.
Discount promotions have also been further exploited by the organization whereby various discounts may get administered on various days of the week.
Conclusion
About a decade ago, Dominos was recognized as a poor man’s Pizza Hut; today, however, the organization remains one of the largest fast-food chains in the world, with over 6 percent rise in sales across the globe; along with a robust vision to expand its global footprint to twenty-five stores by 2052. The company has increased its supply chains and created a robust digital presence, and recently, converted to whole wheat in a bid to promote health awareness among its consumers. And thanks to the company’s commendable teams, no other fast-food organization has managed the 30-minute delivery that Dominos has had. Affordable pricing has also been one of the factors that have kept the 70-year-old organization functional. The company has never failed to remind its consumers about its inclusive nature – it respects different cultures as well as its festivals, and often makes efforts to match regional flavors.
References
Constantinides, E. (2002). The 4S web-marketing mix model. Electronic commerce research and applications, 1(1), 57-76.
Išoraitė, M. (2016). Marketing mixes theoretical aspects. International Journal of Research- Granthaalayah, 4(6), 25-37.
Kraak, V. I., Englund, T., Misyak, S., & Serrano, E. L. (2017). A novel marketing mix and choice architecture framework to nudge restaurant customers toward healthy food environments to reduce obesity in the United States. Obesity Reviews, 18(8), 852-868.
Shah, R. B. (2013). Impact of marketing mix elements on customer loyalty: A study of the fast food industry. Prestige International Journal of Management and Research, 6(2/1), 54.
Singh, M. (2012). Marketing mix of 4P’s for competitive advantage. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 3(6), 40-45.